기억력 향상 게임
준비물
| NO | 부품명 | 수량 |
| 1 | 아두이노 UNO R3 | 1 |
| 2 | LCD모듈 | 1 |
| 3 | LED | 4 |
| 5 | 저항(100옴) | 4 |
| 6 | 푸쉬버튼스위치(노브) | 4 |
| 7 | 부저 | 1 |
| 8 | 점퍼케이블 | 25 |
| 9 | 9V 전원(케이블) | 1 |
| 10 | 브레드보드 | 1 |
회로도

코드
LCD 라이브러리를 라이브러리 매니저에서 추가해줍니다.
#include "LiquidCrystal_I2C.h"
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27,16,2);
int buttons[4] = {2, 3, 4, 5};
int leds[4] = {8, 9, 10, 11};
boolean button[4] = {0, 0, 0, 0};
#define buzzer 6
#define levelsInGame 50
//create an array for this game
int bt_simonSaid[100]; //initialise the array
int led_simonSaid[100]; //initialise the array
boolean lost;
int game_play, level, stage;
void setup(){ // the setup function runs once when you press reset or power the board
Serial.begin(9600);
// initialize digital pins as outputs for LEDS in the buttons.
for(int i=0; i<=3; i++) {
pinMode(buttons[i], INPUT_PULLUP);// set the button pins as inputs
pinMode(leds[i], OUTPUT); // set the led pins as outputs
}
pinMode(buzzer, OUTPUT);
lcd.init();// initialize the lcd
lcd.backlight();
lcd.setCursor(0,0);
lcd.print(" Welcome To ");
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print("> Memory Game <");
delay(2000); // Waiting for a while
lcd.clear();
randomSeed(analogRead(0)); //make our random numbers more random
}
void loop() {// the loop function runs over and over again forever
switch(stage){
case 0:
lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Press Red Button");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print(" for Start Game ");
button[0] = digitalRead(buttons[0]);
while(button[0] == HIGH) {
button[0] = digitalRead(buttons[0]);
}
level=1, stage=1, game_play=1;
break;
case 1:
lcd.clear();
//print level on screen
lcd.setCursor(4,0);
lcd.print("Level: ");
lcd.print((level/10)%10);
lcd.print(level%10);
lcd.setCursor(0,1);
lcd.print(" -- Memorize -- ");
delay(1500);
led_simonSaid[level] = random(8, 12); // populate the array with random 'colours'
for(int i=1; i<=level; i++) {
digitalWrite(led_simonSaid[i], HIGH);//turn on the button light
playBuzzer(led_simonSaid[i]-7);
digitalWrite(led_simonSaid[i], LOW);
delay(400);
}
delay(500);
stage=2;
break;
case 2:
stage=3;
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" -- Play -- ");
break;
case 3:
for(int i=0; i<=3; i++){
button[i] = digitalRead(buttons[i]);
if(button[i] == LOW){
bt_simonSaid[game_play] = leds[i];
digitalWrite(leds[i], HIGH);
playBuzzer(i+1); //make the sound of the button pressed - right or wrong
while(button[i] == LOW){
button[i] = digitalRead(buttons[i]);
}
delay(50);
digitalWrite(leds[i], LOW);
game_play++;
if(game_play-1==level){game_play=1;
stage=4;
break;
}
}
}
delay(10);
break;
case 4:
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" Verification ");
delay(1000);
for(int i=1; i<=level; i++){
if(led_simonSaid[i]!=bt_simonSaid[i]){
lost=1;
break;
}
}
if(lost==1)stage=5;
else stage=6;
break;
case 5:
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" !! You Lost !! ");
tone(buzzer, 350); //play game over low tone on buzzer
for(int i=0; i<=3; i++) {
digitalWrite(leds[i], HIGH);
}
delay(1000);
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("!! GAME OVER !!");
noTone(buzzer);
delay(1000);
for(int i=0; i<=3; i++) {
digitalWrite(leds[i], LOW);
}
level=1, stage=0, lost=0;
break;
case 6:
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" ** You Win ** ");
delay(1000);
if(level==levelsInGame){
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Congratulation");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" Level Complete");
delay(1000);
lcd.clear();
level=1;
}else{
if(level<levelsInGame)level++;
}
stage=1;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void playBuzzer(int x) {
tone(buzzer, 650+(x*100));
delay(300);
noTone(buzzer);
}
거짓말 탐지기
GSR(Galvanic Skin Response)는 피부의 전도성 변화를 측정하여 스트레스 또는 감정 변화를 감지하는 데 사용되는 생리학적인 센서입니다. 이 센서는 피부의 땀 분비에 의한 전도성 변화를 감지하여 심리적 및 감정적 반응을 측정합니다.
GSR 센서는 전기 전도도를 측정하는 두 개의 전극으로 구성됩니다. 이 두 전극은 피부와 접촉하여 피부의 전기 전도도를 측정합니다. 피부의 전기 전도도는 피부 상태와 땀 분비량에 따라 변화합니다. 스트레스, 감정적인 긴장, 불안, 혹은 사실을 숨기려는 시도 등으로 인해 신체가 긴장되면, 자동적으로 땀 분비가 증가하게 됩니다. 이에 따라 피부의 전기 전도도가 증가하게 되고, 이러한 변화를 GSR 센서가 감지합니다.
따라서 GSR 센서는 주로 거짓말 탐지 및 감정 인식 분야에서 사용됩니다. 사람이 거짓말을 할 때나 감정적으로 긴장할 때, 피부의 전기 전도도가 증가하므로 이러한 변화를 감지하여 거짓말을 탐지하거나 감정을 분석하는 데 사용될 수 있습니다.
아래는 공식 홈페이지
https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/Grove-GSR_Sensor/
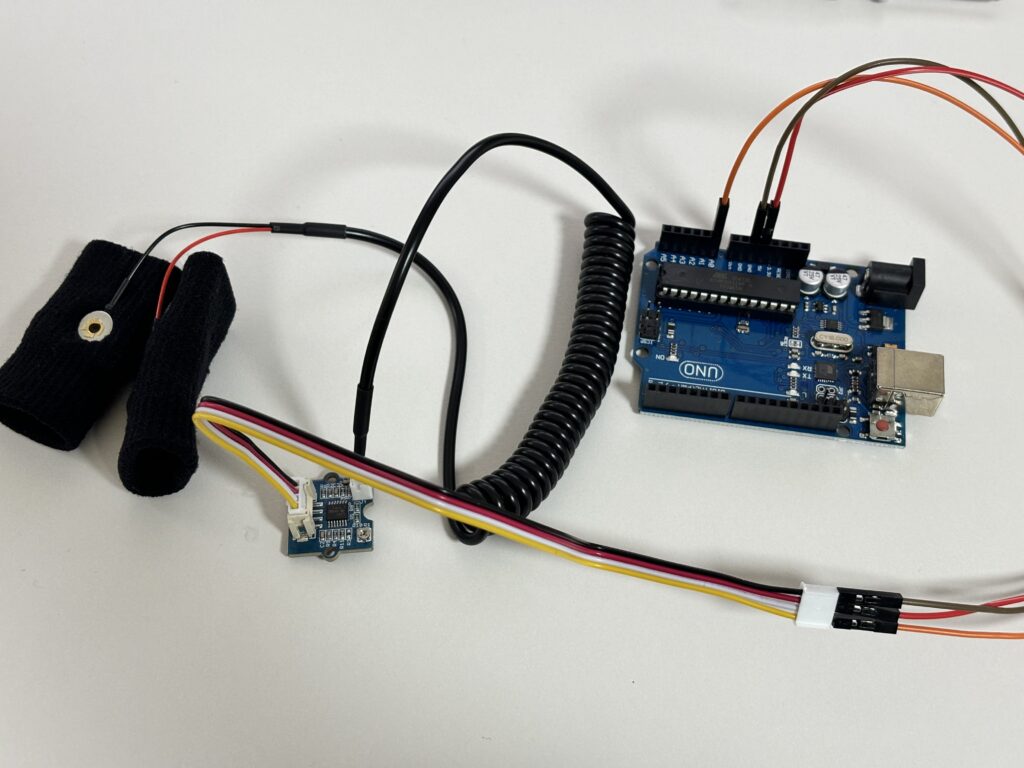
검은색 : GND, 빨간색 : VCC, 노란색 : A0, 흰색 : 연결X
예제 코드
const int GSR=A0;
int sensorValue=0;
int gsr_average=0;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop(){
long sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) //Average the 10 measurements to remove the glitch
{
sensorValue=analogRead(GSR);
sum += sensorValue;
delay(5);
}
gsr_average = sum/10;
Serial.println(gsr_average);
}
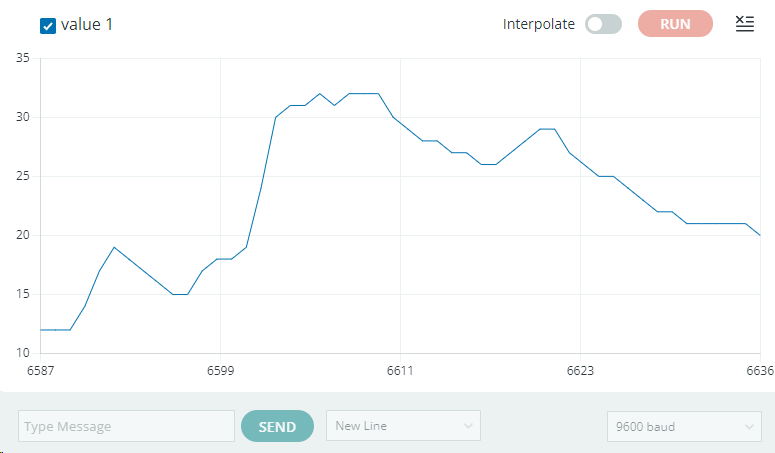
아래와 같이 시리얼 모니터에 그래프가 그려지는것을 확인할 수 있습니다.